
- Permata Kuningan Building Lantai 17,...
- [email protected]
The challenge that we confront in the era of digitization, such data management, are more complicated than previously. Big data, professionalism in data administration, addressing data leaks, real-time data, agile approaches to data management, and other issues are becoming more and more popular. A number of national and international rules also support this issue.
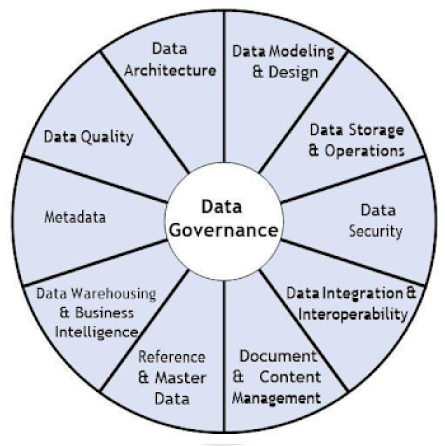
The process of creating data governance rules, which include organizational structure for data management, data architecture and implementation principles, mapping of data entities and organizational data models, and implementation strategies for data governance programs, is known as data governance.
Those sectors are required to ensure the security of data that is regularly managed for business purposes, and this is further encouraged by the existence of several Indonesian regulations that demand ISO/IEC 27001:2022 certification (for instance, the Minister of Communication and Informatics, POJK, PBI, and Government Regulations of the Republic of Indonesia).

As a regulatory provider

Industries subject to Indonesian rules whereby they apply ISO/IEC 27001:2022

Securing patient data

KOMINKO ministerial regulation No.12 of 2016

KOMINKO ministerial regulation No.36 of 2014

Organization that accredited to ISO 27001:2013
An organization’s entire data management strategy should be supported by the function of data governance. Such a framework offers your company a comprehensive method for gathering, managing, safeguarding, and storing data.
As a crucial component of corporate design, the overall data structure and data-related resources
stores, protections, indexes, and makes accessible data from unstructured sources so that it can be integrated and used with structured data.
Analysis, design, structure, testing and maintenance
Utilize standards and data values to manage shared data to eliminate duplication and assure higher data quality.
Structured physical data assets deployment and storage management
Manage analytical data processing and enable access to decision support data for reporting and analysis
Ensuring appropriate privacy, confidentiality
Collection, classification, maintenance, integration, control, management, and delivery of metadata
Purchasing, removing, transforming, moving, delivering, replicating, federating, virtualizing, and providing operational support
Define, monitor, uphold data integrity, and enhance data quality
Data Quality Assurance: Ensuring accurate, consistent, and reliable data supports better decision-making and prevents erroneous conclusions.
Regulatory Compliance: A Data Governance framework helps organizations adhere to these regulations by defining data usage policies, access controls, and audit trails.
Risk Management: Proper Data Governance minimizes the risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, and data loss.
Data Ownership and Accountability: A framework assigns clear roles and responsibilities for data ownership, ensuring that data-related decisions are made by designated individuals or teams.
Data Integration and Interoperability: A Data Governance framework establishes data integration strategies, data sharing protocols, and data exchange standards, promoting interoperability and a holistic view of data.
Data Lifecycle Management: From data creation to archival, a Data Governance framework defines the stages of the data lifecycle and the processes associated with each stage.
Stakeholder Alignment: A well-structured framework fosters communication and collaboration among different business units, IT teams, and stakeholders.
Resource Optimization: Efficient data governance reduces redundancy, avoids data silos, and optimizes data storage and management costs. This is achieved through standar
To increase data quality and instruct all staff to make choice based on data, the Data Governance framework should be implemented as soon as possible.
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR): This regulation applies in the European Union and governs the protection of personal data of EU residents. GDPR requires organizations to have strong control over personal data, including management, protection, and reporting of data breaches.
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA): HIPAA applies in the United States and regulates the security and privacy of patient health data. This regulation requires healthcare organizations to implement technical and organizational measures to safeguard medical data.
Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX): SOX applies in the United States and regulates corporate governance, including financial data management. This regulation emphasizes the accuracy and integrity of data used in financial reporting.
ISO 27001: This is an international standard for information security management. ISO 27001 provides a framework for identifying, managing, and reducing information security risks, including data.
Depending on the requirements of the business, at least four months for implementation